VPNs Corporate Security
In this article, we will explore the topic of corporate security and how VPNs play a vital role in ensuring the safety and privacy of sensitive company information. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, understanding the importance of VPNs in corporate settings is crucial in today’s digital age. From protecting against hacker attacks to enabling secure remote access, we’ll delve into the key benefits and applications of VPNs in corporate security. So, let’s dive in and discover how VPNs can safeguard your company’s sensitive data and maintain a secure network environment.
Overview of VPNs in Corporate Security
What are VPNs?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that allows you to establish a secure and encrypted connection between your device and a remote server over the internet. It creates a private network within a public network, ensuring that your data and online activities are protected from unauthorized access.
In the context of corporate security, VPNs are used to establish secure connections between employees, remote offices, and business partners. By using VPNs, businesses can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their sensitive data and communications.
Importance of VPNs in Corporate Security
In today’s digital age, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, VPNs have emerged as an essential tool for corporate security. They provide a range of benefits that safeguard a company’s valuable assets, including data, resources, and infrastructure.
By implementing VPNs within their network infrastructure, companies can establish secure communication channels, protect against cyber attacks, enable remote access for employees, and maintain anonymity and privacy. These features not only enhance the overall security posture of the organization but also foster a culture of trust and confidence among stakeholders.
Benefits of VPNs in Corporate Security
Enhanced Data Security
One of the primary benefits of using VPNs in corporate security is enhanced data security. By encrypting all the data transmitted between the user’s device and the VPN server, VPNs ensure that sensitive information remains secure even when transmitted over untrusted networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots or shared networks.
Encryption transforms the data into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted by the intended recipient, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized individuals to intercept or tamper with the information. This is particularly important for businesses that deal with confidential customer data, trade secrets, or intellectual property.
Protection from Cyber Attacks
In the constantly evolving threat landscape, businesses face increasingly sophisticated cyber attacks such as hacking, phishing, and malware infections. VPNs play a crucial role in protecting corporate networks and systems from such attacks by creating an additional layer of security.
By routing all internet traffic through the VPN server, businesses can effectively hide their network’s IP address and location from potential attackers. This makes it significantly harder for hackers to target specific resources or exploit vulnerabilities in the network.
Additionally, VPNs often incorporate advanced security features like firewall protection, intrusion detection systems, and anti-malware scanning. These features add an extra level of security by actively monitoring and filtering network traffic for any malicious activities or unauthorized access attempts.
Secure Remote Access
In today’s increasingly remote workforce, secure remote access has become a necessity for many businesses. VPNs enable employees to access corporate resources securely from any location, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected even when accessed from outside the office network.
By establishing a secure connection between the employee’s device and the corporate network, VPNs create a virtual tunnel through which data can securely travel. This allows employees to access files, applications, and other resources without compromising the organization’s security posture.
Whether employees are working from home, traveling, or in remote offices, VPNs provide a seamless and secure way for them to connect to the corporate network and carry out their tasks without exposing sensitive data to potential threats.
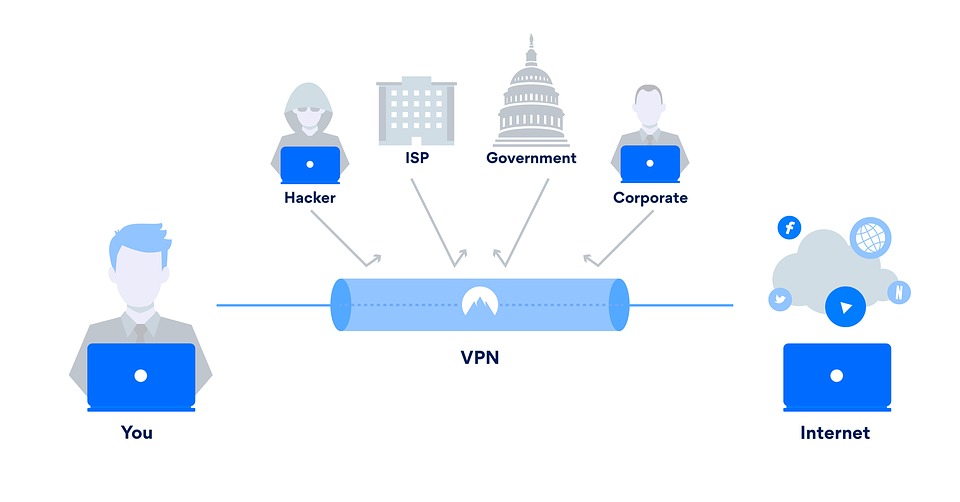
Anonymity and Privacy
In an era where online privacy is frequently compromised, VPNs offer an additional layer of anonymity and privacy. By masking the user’s IP address and encrypting their internet traffic, VPNs prevent malicious actors, internet service providers, or government agencies from monitoring or tracking their online activities.
For businesses, this aspect of VPNs is crucial as it protects sensitive corporate information from being intercepted or monitored by competitors or other external parties. By ensuring the privacy of their online communications, businesses can mitigate the risk of industrial espionage, unauthorized surveillance, or data leakage.
Moreover, VPNs also help maintain compliance with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), by safeguarding the privacy and confidentiality of personal and sensitive data.
VPNs and Data Encryption
How VPNs Encrypt Data
At the heart of VPNs’ ability to provide secure communication lies data encryption. VPNs use encryption protocols to transform the data packets into encrypted codes that can only be decrypted by the recipient.
When a user attempts to access a resource through a VPN, an encryption process is initiated. The user’s device encrypts the data by applying complex mathematical algorithms, ensuring that it becomes unintelligible to anyone without the decryption key. This encrypted data is then transmitted to the VPN server.
Once the encrypted data reaches the VPN server, it is decrypted using the same encryption key. From there, the VPN server forwards the decrypted data to the appropriate destination, whether it’s a website, server, or another network device. The response follows the same path in reverse, ensuring end-to-end encryption throughout the communication process.
Types of Encryption Algorithms Used
VPN encryption relies on various encryption algorithms to secure the transmitted data. These algorithms use complex mathematical calculations to scramble the data in a highly secure manner.
Some of the commonly used encryption algorithms in VPNs include:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): AES is widely considered the gold standard of encryption algorithms. It offers a high level of security and is commonly used by VPNs to protect sensitive data.
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm commonly used for key exchange during the VPN connection setup process. It ensures secure communication by encrypting the encryption keys used during the session.
- 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard): 3DES is an older encryption algorithm that applies the Data Encryption Standard (DES) cipher three times to each data block. While it is still in use, it is gradually being phased out in favor of more secure algorithms.
- Blowfish: Blowfish is a symmetric-key block cipher that has been widely used in VPN encryption. While it is considered secure, it is being gradually replaced by more advanced algorithms.
It’s important for businesses to choose VPN providers that use strong encryption algorithms to ensure the highest level of data protection. The use of weak or obsolete encryption algorithms can potentially expose the network to security vulnerabilities.
Importance of Strong Encryption
Strong encryption is a cornerstone of VPN security. It ensures that the data transmitted over the VPN is secure and protected from unauthorized access or interception.
By using strong encryption algorithms, VPNs make it extremely difficult for attackers to decrypt any intercepted data, even if they manage to intercept it successfully. This effectively renders the intercepted data useless to potential attackers, preserving the confidentiality and integrity of the transmitted information.
Strong encryption also protects against passive eavesdropping, where attackers attempt to capture and analyze network traffic without altering it. By encrypting the data, VPNs prevent attackers from gaining access to sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, or other confidential business information.
Furthermore, strong encryption adds an additional layer of authentication by ensuring that the data received by the VPN server is from the intended source. This helps prevent attacks such as man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker intercepts the communication and poses as the intended recipient.
In summary, strong encryption is critical for VPNs as it guarantees the security and privacy of data transmitted over the network. It provides an effective defense against unauthorized access, data breaches, and interception of sensitive information.
Types of VPNs for Corporate Security
Remote Access VPNs
Remote Access VPNs are the most commonly used type of VPNs in corporate environments. They allow employees to securely access the corporate network from remote locations, such as home offices or while traveling.
Remote Access VPNs create a secure tunnel between the employee’s device and the corporate network, extending the corporate network’s reach to the remote device. This allows employees to access corporate resources, files, and applications just as they would if they were physically present in the office.
By encrypting all data transmitted between the user’s device and the corporate network, Remote Access VPNs ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the data, even when accessed over untrusted networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots.
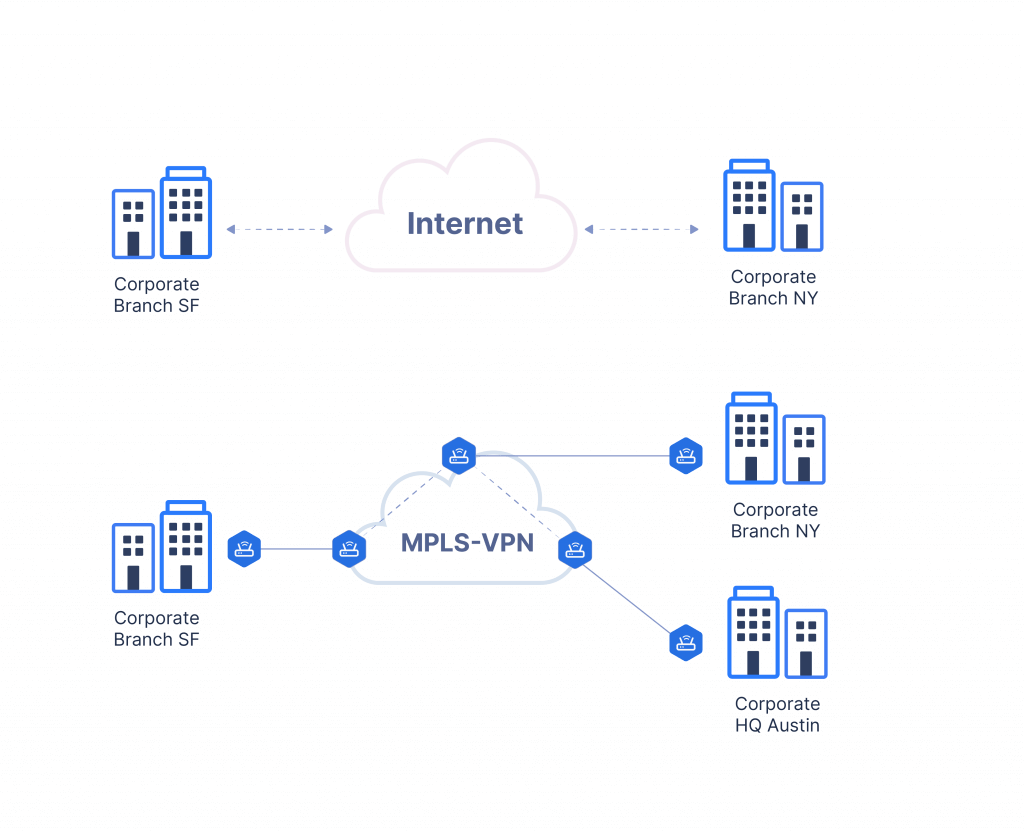
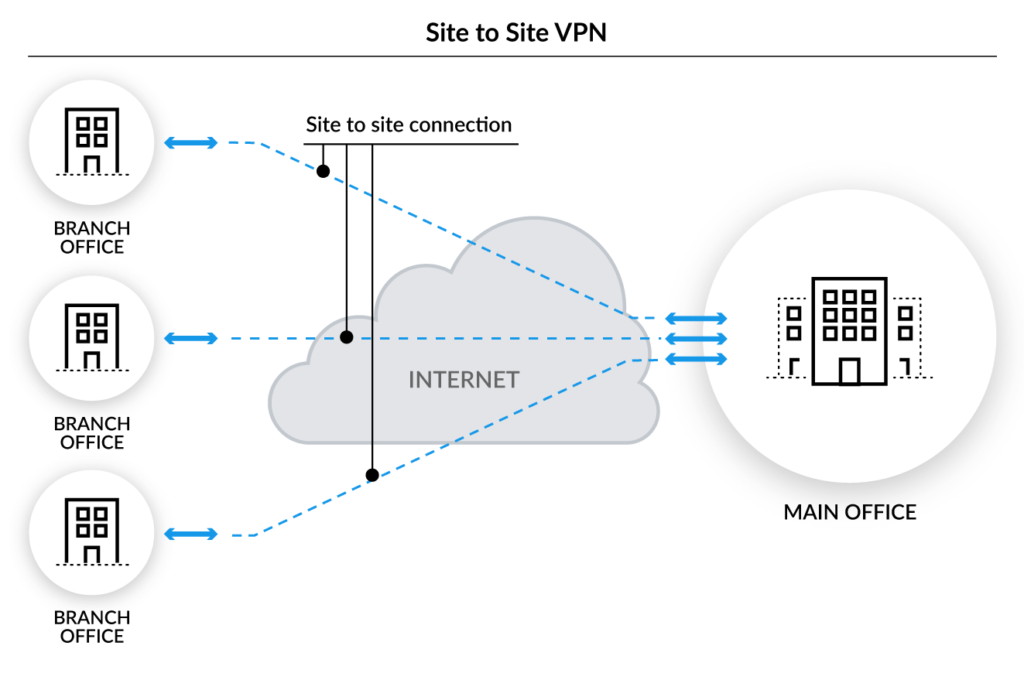
Site-to-Site VPNs
Site-to-Site VPNs, also known as router-to-router VPNs, are used to establish secure connections between multiple corporate networks or branch offices. They enable the secure transmission of data between different networks, regardless of their physical location.
With Site-to-Site VPNs, each participating network has a VPN gateway or router that handles the encryption and decryption of data. When two networks need to communicate securely, the VPN gateways establish a secure tunnel, allowing traffic to be securely transmitted between the networks.
Site-to-Site VPNs are commonly used in organizations with multiple branch offices or locations, enabling seamless communication and data sharing between them. They provide a cost-effective and efficient way to connect geographically dispersed networks while ensuring the security of transmitted data.
Mobile VPNs
Mobile VPNs are specifically designed to provide secure connectivity for mobile devices, such as smartphones or tablets. They allow employees to access corporate resources and applications securely, even when on the go.
Mobile VPNs create a secure tunnel between the mobile device and the corporate network, encrypting all data transmitted between the two. This ensures that sensitive corporate information remains protected, even when accessed from potentially unsecured public networks.
Mobile VPNs often incorporate additional security features, such as device-level authentication and data loss prevention, to further enhance the security of mobile communications. These features help protect against potential threats, such as device theft or unauthorized access to corporate data in case of a lost or stolen device.
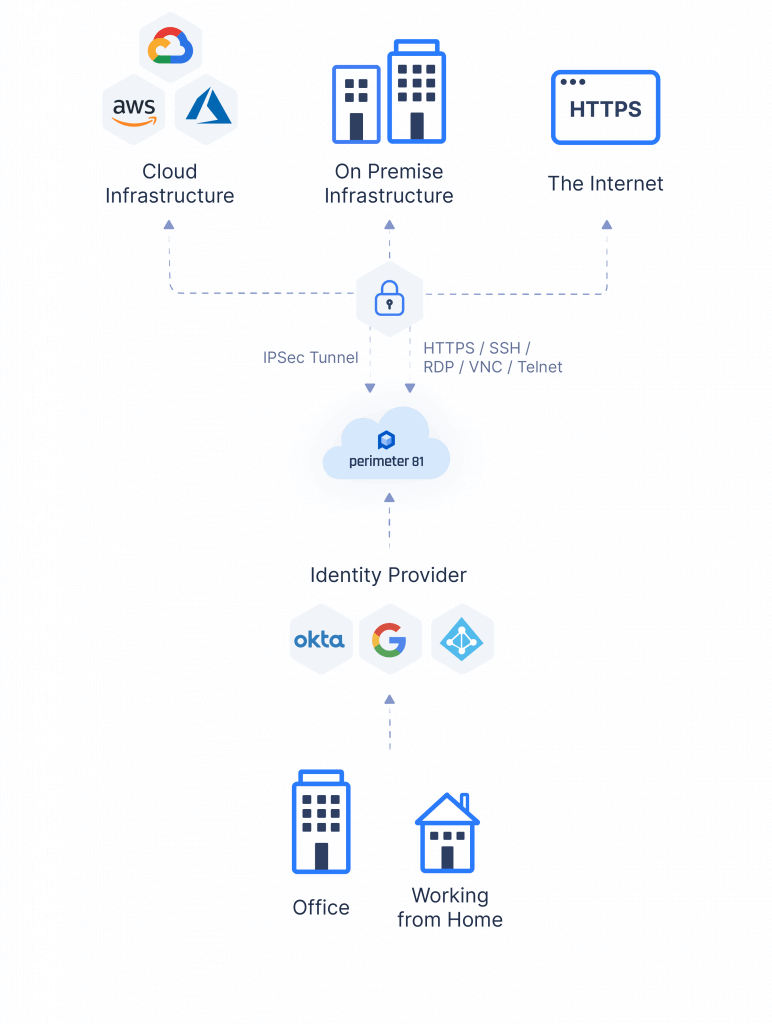
Cloud VPNs
Cloud VPNs, also known as Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) or VPN-as-a-Service, provide secure connectivity and communication between corporate networks and cloud service providers. They enable businesses to extend their existing network infrastructure into the cloud, ensuring secure data transmission and access to cloud-based resources.
With Cloud VPNs, businesses can securely connect their on-premises network to cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. This allows them to leverage the scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency of cloud services while maintaining a high level of security for their data and resources.
Cloud VPNs rely on secure network connections, either through dedicated connections or encrypted connections over the internet, to establish the link between the corporate network and the cloud service provider. This ensures that all data transmitted between the two entities remains encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
Considerations when Choosing a VPN for Corporate Security
Security Protocols and Encryption Strength
When choosing a VPN for corporate security, one of the most crucial considerations is the type of security protocols and encryption strength offered by the VPN provider.
Different VPNs support various security protocols, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some common VPN protocols include OpenVPN, IPSec, and SSL/TLS. It is important to select a VPN that offers protocols that are known for their security, reliability, and compatibility with various devices and operating systems.
Additionally, the encryption strength provided by the VPN is vital. As mentioned earlier, strong encryption plays a pivotal role in preserving the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over the VPN. Look for VPN providers that use industry-standard encryption algorithms like AES-256, which is considered highly secure.
Server Locations and IP Addresses
The server locations and IP addresses offered by a VPN provider are essential considerations, especially for businesses with a global presence or employees who frequently travel abroad.
Having VPN servers located in multiple countries allows businesses to establish secure connections from various geographic locations. This ensures that employees or remote offices can access the VPN servers with minimal latency and optimal performance.
Furthermore, the VPN provider should offer a sufficient number of IP addresses for their servers. This prevents IP address sharing among multiple users, reducing the risk of potential IP address conflicts or unauthorized access to the network.
Logging Policies
VPN providers typically have logging policies that define what user information they retain and how long they retain it. It is crucial to choose a VPN provider with a strict no-logs policy that ensures they do not retain any personally identifiable information or user activity logs.
A no-logs policy guarantees the privacy and anonymity of users by preventing the VPN provider from storing information that could potentially be used to monitor or track their online activities. This is particularly important for businesses that handle sensitive corporate data or need to adhere to strict data protection regulations.
Compatibility and Ease of Use
When selecting a VPN for corporate security, compatibility and ease of use are paramount. The VPN should be compatible with various operating systems and devices used within the organization, including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
Additionally, a user-friendly interface and intuitive configuration options are essential for smooth deployment and user adoption. The VPN client should be easy to install, configure, and maintain, minimizing the need for extensive technical support or training.
By choosing a VPN that is compatible with existing infrastructure and user devices and offers a seamless user experience, businesses can maximize the effectiveness and efficiency of their corporate security measures.
Implementing VPNs in Corporate Networks
Establishing VPN Connections
Implementing VPNs in corporate networks typically involves setting up and configuring VPN connections for employees, remote offices, and business partners. This process involves the following steps:
- VPN Infrastructure Planning: Define the scope and requirements of the VPN infrastructure, considering factors such as the number of users, remote offices, and anticipated traffic volume.
- VPN Server Setup: Set up dedicated VPN servers or configure existing network devices as VPN servers. Ensure that the servers are properly secured and meet the necessary performance requirements.
- User Authentication: Establish a user authentication mechanism, such as username/password or digital certificates, to verify the identity of VPN users before granting them access.
- VPN Client Setup: Install and configure VPN client software on user devices, such as laptops, smartphones, or tablets. Ensure that the client software is compatible with the user’s operating system and offers a user-friendly interface.
- Connection Configuration: Configure the VPN client settings, including server IP addresses, security protocols, and encryption settings. Establish the necessary connection parameters, such as split tunneling or full tunneling, based on business requirements.
- Testing and Deployment: Test the VPN connections to ensure they are working correctly and meeting the required security standards. Deploy the VPN client software and connect users to the VPN infrastructure.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the VPN infrastructure, including server performance, user activity, and security logs. Perform routine maintenance tasks, such as software updates or security patching, to ensure the continued effectiveness of the VPN.
Network Infrastructure Requirements
Implementing VPNs in corporate networks requires certain network infrastructure requirements to ensure a secure and seamless VPN experience.
First and foremost, a stable and reliable internet connection is essential. VPNs transmit data over the internet, so a network that experiences frequent outages or connectivity issues may result in unreliable VPN connections.
Businesses also need to have dedicated VPN servers or compatible network devices capable of handling the VPN traffic. These servers should have adequate processing power, memory, and network bandwidth to accommodate the expected number of VPN users and the associated traffic volume.
Additionally, VPN implementation may require adjustments to the existing network infrastructure, such as configuring firewalls or network address translation (NAT) rules to allow VPN traffic to pass through. It’s important to consult with network administrators or IT experts to ensure that the network infrastructure can support VPN connectivity.
Managing VPN Users and Permissions
A key aspect of implementing VPNs in corporate networks is managing VPN users and their permissions. This involves creating user accounts, defining access rights, and ensuring that only authorized personnel have VPN access.
User accounts should be created for each individual who requires VPN access, with unique usernames and strong passwords. To enhance security, businesses can implement additional authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication, to verify the identity of VPN users.
Access rights should be carefully defined based on the individual user’s role and responsibilities within the organization. Different levels of access permissions can be assigned, ensuring that users can only access the resources necessary for their job functions.
Furthermore, user access should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect organizational changes, such as employee onboarding, terminations, or role changes. This ensures that only current employees have access to the corporate network via the VPN and minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
VPN Client Installation and Configuration
The installation and configuration of VPN client software on user devices is a critical step in implementing VPNs in corporate networks. This process typically involves the following steps:
- Installation: Deploy the VPN client software to user devices using centralized deployment tools or individual installation packages. Ensure that the installation process is user-friendly and includes clear instructions for the end users.
- Configuration: Configure the VPN client settings to establish a secure connection to the corporate network. This includes specifying the VPN server’s IP address, security protocols, encryption settings, and any other necessary connection parameters.
- User Authentication: Set up the necessary user authentication mechanisms, such as username/password or digital certificates, on the VPN client. Verify that the client is correctly configured to prompt users for their credentials before establishing the VPN connection.
- Testing: Test the VPN client installation and configuration to ensure that users can successfully establish a secure VPN connection. Verify that all necessary resources, such as file shares or applications, are accessible via the VPN.
- Documentation and Support: Provide clear documentation and user support resources to assist employees in installing and configuring the VPN client software. This includes step-by-step guides, FAQs, or even training sessions to ensure that users understand how to use the VPN effectively and securely.
By following a well-defined and documented process for installing and configuring VPN client software, businesses can ensure that their employees can easily and securely connect to the corporate network.
Best Practices for Using VPNs in Corporate Environments
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are an essential practice for maintaining the effectiveness of VPNs in corporate environments. These audits should encompass both the VPN infrastructure and the associated security controls and policies.
Audits can include reviewing VPN server configurations, encryption settings, and security protocol implementations. It’s crucial to ensure that the VPN infrastructure adheres to industry best practices and meets the organization’s security requirements.
Furthermore, regular auditing of user accounts and access permissions is critical. This ensures that only authorized individuals have VPN access and that access rights are aligned with current job responsibilities.
Periodic VPN Client Updates
Keeping VPN client software up to date is important for maintaining the security and functionality of VPN connections. VPN providers often release updates and patches that address security vulnerabilities or introduce new features.
Businesses should have a process in place to periodically review and apply VPN client updates. This includes ensuring that all user devices are running the latest version of the VPN client software and that any necessary configuration adjustments are made to accommodate the updates.
By regularly updating the VPN client software, businesses can ensure that their employees are benefiting from the latest security enhancements and improvements in VPN technology.
Employee Training and Awareness
Training employees and raising awareness about VPN usage and best practices is crucial for maintaining a secure corporate environment. Many security incidents can be attributed to human error or lack of knowledge regarding secure VPN practices.
Businesses should provide training sessions or workshops to educate employees about the importance of VPNs, how to properly use VPN connections, and potential security risks associated with VPN usage. This includes topics such as choosing secure passwords, avoiding phishing attacks, and properly configuring VPN client software.
Regular communication and reminders about VPN usage policies and best practices can also help reinforce secure behaviors among employees. By fostering a culture of security-consciousness, businesses can minimize the risk of VPN-related security incidents.
Secure Connection Sharing
It is essential to educate employees about the risks associated with sharing VPN connections with unauthorized individuals. While VPNs are designed to establish secure and encrypted connections, sharing VPN credentials or connection details with others can potentially compromise the security of the network.
Employees should be made aware of the importance of keeping their VPN credentials confidential and not sharing them with anyone, including family members, friends, or colleagues. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to the corporate network and helps maintain the integrity and security of the VPN connections.
Additionally, businesses should consider implementing measures to prevent unauthorized sharing of VPN connections, such as limiting the number of simultaneous VPN connections per user or implementing session timeout features that automatically disconnect idle connections.
By promoting secure connection sharing practices, businesses can ensure that VPN usage remains compliant with security policies and reduce the risk of compromising the confidentiality and integrity of corporate data.
Challenges and Limitations of VPNs in Corporate Security
Managing VPN Performance
Managing VPN performance can be a challenging aspect of implementing VPNs in corporate security. VPNs can introduce additional latency and bandwidth constraints, which can impact the performance of data-intensive applications or services.
To overcome these challenges, businesses should carefully consider their network infrastructure’s capacity and scalability to handle the anticipated VPN traffic. This may involve upgrading network connections, increasing server resources, or implementing traffic management and optimization techniques.
Monitoring and performance tuning of the VPN infrastructure can help identify bottlenecks and address any performance issues promptly. This may involve optimizing encryption settings, adjusting the VPN client configuration, or implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize VPN traffic.
Verifying VPN Service Providers
Selecting a trustworthy and reliable VPN service provider can be a challenge, given the numerous options available in the market. It is crucial to thoroughly research and evaluate VPN providers before making a decision.
Businesses should consider factors such as the provider’s reputation, track record, and adherence to security best practices. It is also important to review their privacy policies and user agreements to ensure that they align with the organization’s security and compliance requirements.
Performing due diligence, including reading reviews and seeking recommendations, can help identify reputable VPN service providers. Additionally, consulting with security professionals or engaging the services of a trusted third-party can provide valuable insights and guidance during the selection process.
Over-reliance on VPNs
While VPNs are an integral part of corporate security, businesses must avoid over-reliance on VPNs as the sole security measure. VPNs are not a silver bullet solution and should be complemented by other security controls and measures.
To ensure comprehensive security, businesses should adopt a multi-layered approach that includes technologies such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and user access controls. This defense-in-depth strategy provides added protection against various threats and reduces dependency on VPNs alone.
Furthermore, businesses should continuously assess and update their security posture by staying informed about emerging threats, industry best practices, and the latest security technologies. This allows for a proactive and adaptive response to evolving security challenges.
Mitigating Human Error
Human error remains a prevalent challenge in corporate security, and VPN usage is no exception. Employees may inadvertently compromise the security of VPN connections through actions such as choosing weak passwords, falling victim to phishing attacks, or failing to update VPN client software.
To mitigate the risk of human error, businesses should prioritize employee training and awareness programs that educate users about secure VPN practices and potential risks. Emphasizing the importance of strong passwords, identifying and reporting phishing attempts, and promptly installing software updates can help minimize the impact of human error.
Additionally, implementing strict access controls and strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access resulting from human error.
Risks of Not Using VPNs in Corporate Security
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Not using VPNs in corporate security exposes businesses to the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Without a secure connection, sensitive data transmitted over the internet can be intercepted by malicious actors, leading to unauthorized disclosure, modification, or theft of sensitive information.
Data breaches can result in severe financial and reputational damage to an organization, potentially leading to lost customer trust, legal consequences, and regulatory penalties. By not utilizing VPNs, businesses significantly increase their vulnerability to such incidents.
Exposure to Malware and Ransomware
Without a VPN, corporate networks and devices are more susceptible to malware infections and ransomware attacks. Unsecured connections can serve as vectors for delivering malicious software to vulnerable systems, potentially compromising the entire network.
VPN encryption helps prevent unauthorized access to corporate networks and ensures that sensitive information is kept secure. By not using VPNs, businesses leave themselves open to attacks that can lead to costly cleanup efforts, data loss, and operational disruptions.
Loss of Sensitive Information
Not utilizing VPNs increases the risk of sensitive information loss. Employees accessing corporate resources or transmitting confidential data over unsecured networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots, are more vulnerable to eavesdropping and interception.
Sensitive information can be compromised, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage to the organization. The loss of intellectual property, trade secrets, or personally identifiable information (PII) can have long-lasting and far-reaching consequences.
Legal and Compliance Issues
Failing to use VPNs in corporate security can lead to legal and compliance issues, particularly in heavily regulated industries. Many regulations, such as the GDPR, HIPAA, or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), require organizations to implement appropriate security measures to safeguard sensitive data.
Not utilizing VPNs can result in non-compliance with these regulations, leading to legal consequences, financial penalties, and damage to an organization’s reputation. Businesses that handle sensitive data must ensure they have adequate security measures in place, including the use of VPNs, to comply with applicable regulations.
Future Trends in VPNs for Corporate Security
Improvements in VPN Technologies
As the importance of VPNs in corporate security continues to grow, ongoing advancements in VPN technologies can be expected. These improvements aim to enhance security, performance, and user experience.
Future VPN technologies may include more robust encryption algorithms, increased compatibility, and streamlined deployment and configuration options. VPN providers will likely continue to invest in research and development to counter evolving cyber threats and provide efficient solutions for corporate security needs.
Integration with Advanced Security Measures
VPN technologies are likely to integrate more seamlessly with advanced security measures, such as threat intelligence, machine learning, and behavior analytics. This integration will enable VPNs to better detect and prevent advanced threats in real-time, enhancing the overall security posture of corporate networks.
By leveraging advanced security measures alongside VPNs, businesses can develop robust defense systems that proactively identify and respond to potential security breaches and ensure the continued protection of their sensitive data and resources.
Emergence of Zero Trust Networks
The concept of Zero Trust Networks is gaining traction in corporate security. Zero Trust Networks operate on the philosophy of “never trust, always verify,” meaning that every user and device trying to access corporate resources is continuously authenticated and authorized, regardless of their location or network connection.
VPNs are expected to play a crucial role in the implementation of Zero Trust Networks by securing remote access and establishing secure tunnels for user connections. This allows businesses to implement a more granular and fine-tuned security model that ensures secure access to resources without the need for a traditional perimeter-based approach.
The ongoing progress in VPN technologies, integration with advanced security measures, and the emergence of Zero Trust Networks will shape the future of VPNs in corporate security, ensuring that businesses have robust and efficient tools to protect their sensitive data and resources.
In conclusion, VPNs are an indispensable component of corporate security in today’s digital landscape. They provide enhanced data security, protection from cyber attacks, secure remote access, and anonymity and privacy. By encrypting data, using strong encryption algorithms, and offering various types of VPNs, businesses can establish secure connections within their networks and beyond. However, careful consideration must be given to security protocols, server locations, logging policies, and compatibility when choosing a VPN for corporate security. Implementing VPNs requires establishing VPN connections, meeting network infrastructure requirements, managing users and permissions, and configuring VPN client software. Best practices such as regular security audits, periodic VPN client updates, employee training and awareness, and secure connection sharing can optimize the usage of VPNs in corporate environments. Challenges and limitations, such as managing VPN performance, verifying VPN service providers, over-reliance on VPNs, and mitigating human error, must be addressed. Not using VPNs exposes businesses to risks such as data breaches, exposure to malware and ransomware, loss of sensitive information, and legal and compliance issues. As VPN technologies continue to improve, integrating with advanced security measures and enabling the implementation of Zero Trust Networks, the future of VPNs in corporate security looks promising. By staying informed of trends and advancements in VPN technology, businesses can ensure the ongoing effectiveness and resilience of their corporate security measures.