History Of VPNs
If you’ve ever wondered about the origins of VPNs and how they have evolved over time, this article is for you. We’ll explore the fascinating history of VPNs, from their humble beginnings as a tool for remote access to their widespread use in today’s digital world. Whether you’re a VPN novice or a seasoned user, this article will provide valuable insights into the development and application of VPN technology in various settings, including gaming, corporate security, and beyond. So, buckle up and prepare to embark on a journey through the history of VPNs.
1. Origins of VPNs
VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, have come a long way since their inception. Let’s take a stroll down memory lane and explore their origins.
Early Development
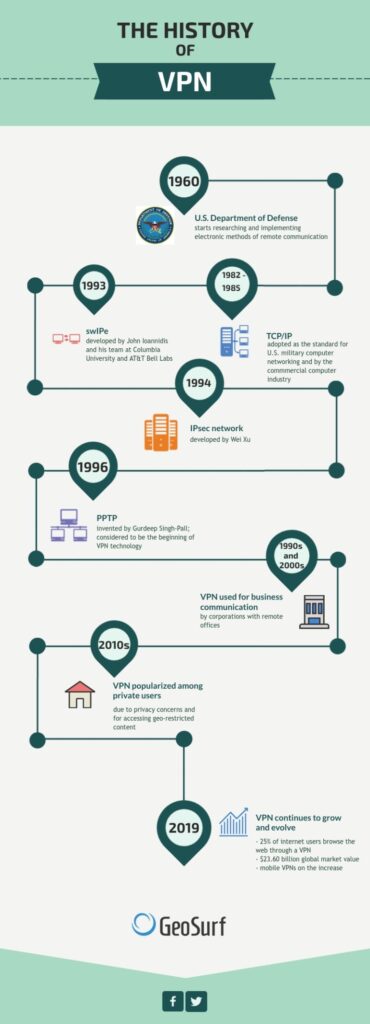
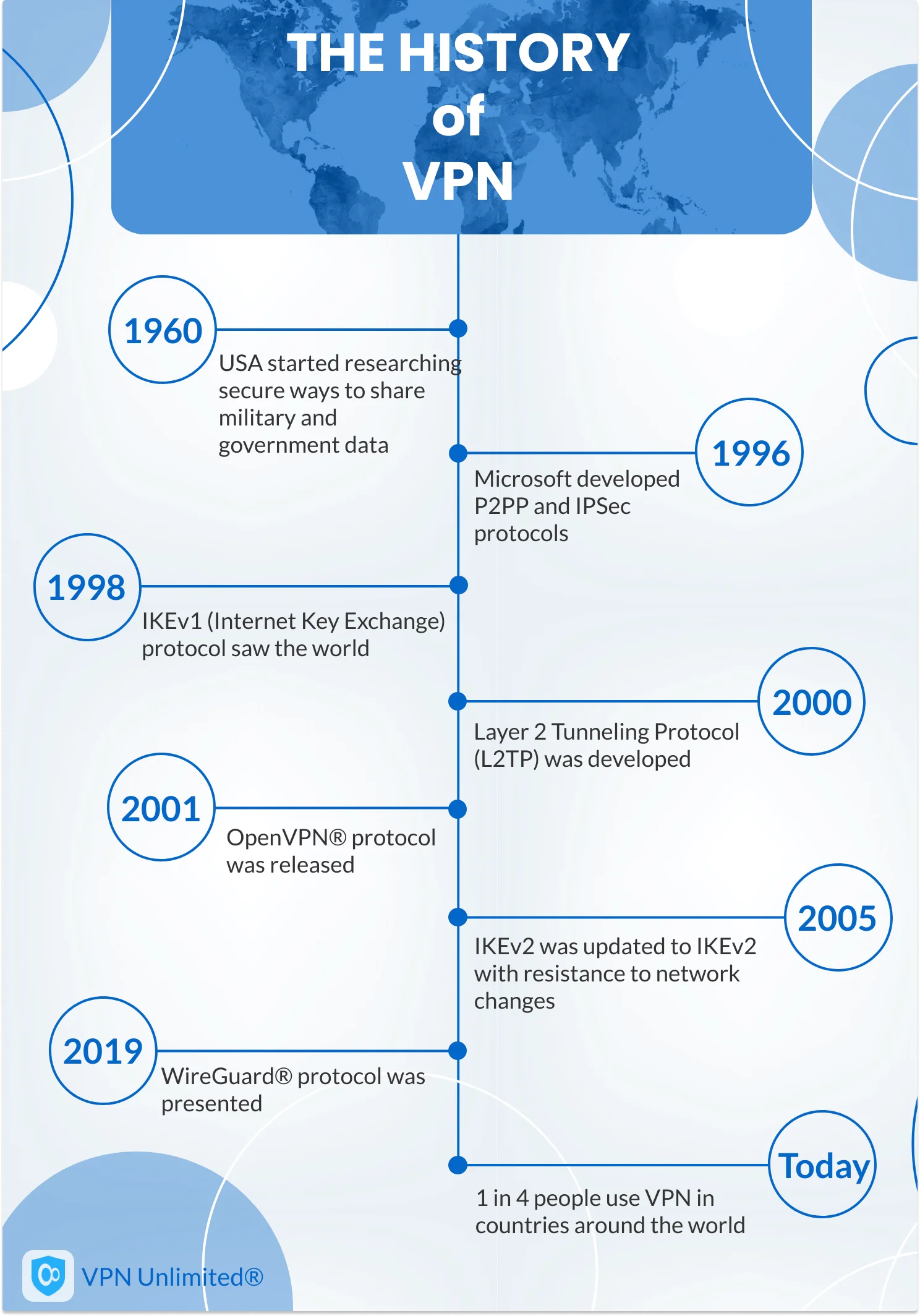
The birth of VPNs can be traced back to the late 1960s when researchers were looking for ways to connect computers over long distances. One of the earliest developments in this field was the creation of X.25 networks, which utilized packet-switching technology to transmit data between different devices. This laid the foundation for the future development of VPNs.
X.25 Networks
X.25 networks, developed in the 1970s, allowed for the establishment of virtual circuits between remote computers. These networks provided a reliable and secure way to transmit data, making them an important stepping stone in the evolution of VPN technology. While X.25 networks were primarily used by large corporations and government agencies, they paved the way for the widespread adoption of VPNs.
ATMs and Frame Relay
In the 1980s, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Frame Relay emerged as new networking technologies. ATM networks provided high-speed transmission capabilities, while Frame Relay offered a more cost-effective alternative for data transmission. These advancements played a crucial role in the development of VPNs by providing faster and more efficient communication protocols.
Emergence of the Internet
The emergence of the internet in the 1990s revolutionized the way people communicated and accessed information. With the widespread adoption of the internet, the need for secure and private communication became increasingly important. This led to the development of VPN technologies that provided a secure tunnel for data transmission over public networks, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
2. Development of VPN Technology
Over the years, several key technologies have contributed to the development of VPNs. Let’s delve into each of them.
X.509 Certificate
The X.509 certificate, introduced in the late 1980s, played a significant role in the development of secure communication protocols. It provided a standardized format for digital certificates, enabling the authentication of network entities. X.509 certificates are still widely used today in various VPN implementations.
SSL VPN
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN, introduced in the mid-1990s, offered a secure way to access internal network resources over the internet. SSL VPNs utilized the SSL/TLS protocol to establish an encrypted connection between the client and the VPN gateway. This allowed remote users to securely access corporate networks without the need for dedicated VPN software.
IETF IPsec
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) developed IPsec, or Internet Protocol Security, as a standard protocol suite for securing IP communications. IPsec provides encryption, authentication, and integrity verification for network traffic, making it one of the most widely used VPN protocols. IPsec operates at the network layer of the OSI model and is compatible with various network technologies.
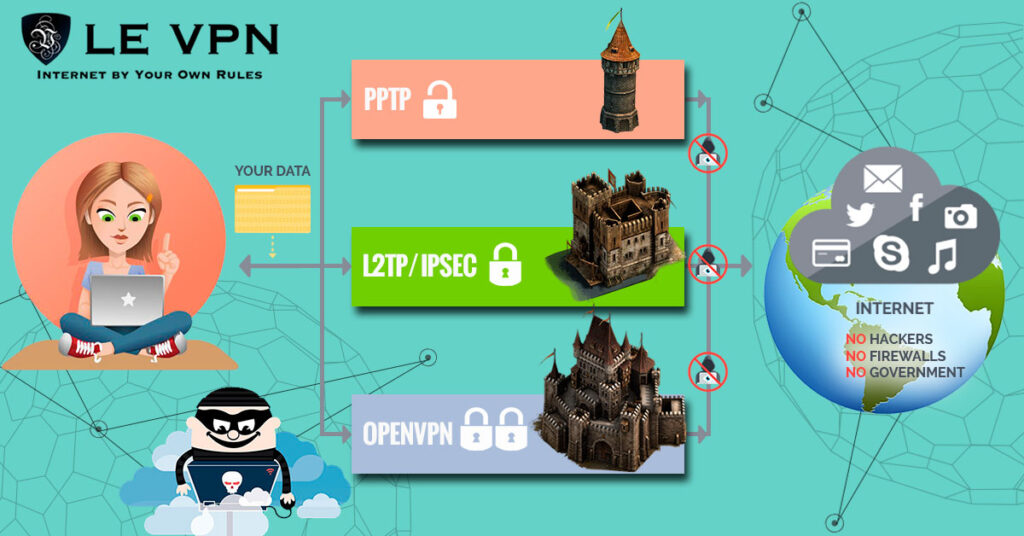
L2TP
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) combines the best features of two other VPN protocols – PPTP and L2F. L2TP, introduced in the late 1990s, uses IPsec for encryption and authentication, enhancing security. It operates at the data link layer of the OSI model and supports multiple authentication methods. L2TP is widely supported by both VPN clients and servers, making it a popular choice for VPN implementations.
PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) was one of the earliest VPN protocols to gain widespread popularity. It provided a secure tunnel for data transmission by encapsulating PPP packets within IP packets. PPTP was very easy to set up and supported by a wide range of operating systems. However, due to security vulnerabilities discovered in the protocol, its usage has declined in recent years.
VPN Concentrators
VPN concentrators, also known as VPN gateways, are hardware or software devices that allow multiple VPN connections to be aggregated and managed centrally. They provide scalability and efficient routing of VPN traffic, making it possible for organizations to support a large number of VPN users. VPN concentrators play a crucial role in the scalability and management of VPN deployments.
3. Evolution of VPN Protocols
As technology advanced, so did the protocols used in VPNs. Let’s explore the evolution of VPN protocols.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer protocol that provides a standard method for establishing a direct connection between two nodes. PPP served as the foundation for various VPN protocols, including PPTP and L2TP. It provided a reliable means of encapsulating data packets and supporting multiple network protocols.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), as mentioned earlier, combined the best features of PPTP and L2F (Layer Two Forwarding). L2TP was designed to provide a secure tunnel for carrying PPP traffic over IP networks. It added the security and authentication features of IPsec to enhance the overall security of VPN connections.
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a suite of protocols used to secure IP communications. IPsec provides encryption, authentication, and integrity verification for data transmitted over an IP network. It operates at the network layer of the OSI model and can be used to establish site-to-site VPNs or remote access VPN connections.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), now succeeded by Transport Layer Security (TLS), is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication over the internet. SSL/TLS VPNs establish an encrypted connection between the client and the VPN gateway, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted between them. SSL/TLS VPNs are widely used for remote access to corporate networks.
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) succeeded SSL as the primary protocol for secure communication over the internet. TLS provides encryption, authentication, and integrity verification for data transmitted between client and server. It is used to secure various internet protocols, including HTTPS, SMTP, FTPS, and VPNs. TLS-based VPNs offer a high level of security and are widely supported by modern VPN clients.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol that utilizes SSL/TLS encryption. It is highly configurable and supports a wide range of authentication methods, making it a popular choice for VPN implementations. OpenVPN is compatible with both TCP and UDP protocols and can be used on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile platforms.
WireGuard
WireGuard is a relatively new VPN protocol that aims to provide simplicity, speed, and state-of-the-art cryptography. It operates at the network layer, similar to IPsec, and is designed to be lightweight and efficient. WireGuard has gained traction due to its ease of implementation and strong security features, making it a promising contender in the VPN world.
4. Popular VPN Services
Now that we’ve explored the technology behind VPNs, let’s take a look at some popular VPN service providers.
ExpressVPN
Known for its robust security features and fast performance, ExpressVPN is a popular choice among VPN users. It offers a wide range of server locations and supports multiple VPN protocols, including OpenVPN, IPsec, and SSTP. ExpressVPN also provides user-friendly applications for various devices and a strict no-logs policy, ensuring user privacy.
NordVPN
NordVPN is renowned for its vast server network, which spans across numerous countries. It offers strong encryption, obfuscation technology for bypassing censorship, and a user-friendly interface. NordVPN also provides additional features like Double VPN and Onion Over VPN, enhancing user privacy and anonymity.
Surfshark
Surfshark is a relatively new VPN service that has quickly gained popularity. It offers unlimited simultaneous connections, making it an excellent choice for users with multiple devices. Surfshark boasts strong encryption, a strict no-logs policy, and a unique MultiHop feature that routes traffic through multiple servers for added privacy.
CyberGhost
CyberGhost is known for its user-friendly interface and wide range of server locations. It offers strong encryption, DNS and IP leak protection, and an automatic kill switch. CyberGhost also provides dedicated profiles for streaming, torrenting, and gaming, making it a versatile choice for VPN users.
Private Internet Access (PIA)
Private Internet Access (PIA) is a well-established VPN provider known for its affordability and strong security features. It offers a large number of servers in diverse locations, enabling users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content from around the world. PIA also supports multiple VPN protocols and provides robust encryption for user privacy.
5. VPN Applications in Corporate Security
VPNs play a crucial role in enhancing corporate security. Let’s explore some common applications of VPNs in corporate environments.
Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPNs allow employees to securely connect to their organization’s internal network from remote locations. By establishing an encrypted connection over the internet, remote access VPNs enable employees to access company resources, such as files, databases, and applications, as if they were directly connected to the office network. This promotes productivity and flexibility while maintaining the security of sensitive information.
Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPNs, also known as router-to-router VPNs, connect multiple networks located in separate physical locations. These VPNs enable organizations with multiple branches or offices to securely communicate and share resources over the internet. Site-to-Site VPNs establish encrypted tunnels between routers, allowing for seamless integration of networks and secure data transmission.
Extranet-based VPN
An extranet-based VPN extends the corporate network to trusted business partners, suppliers, or customers. It allows organizations to securely share resources and collaborate with external entities while maintaining strict access controls and data privacy. Extranet-based VPNs provide a secure and controlled environment for sharing sensitive information and conducting business transactions.
Mobile VPN
Mobile VPNs cater to the increasing demand for secure connectivity on mobile devices. These VPNs enable employees or individuals to securely access corporate resources or browse the internet while connected to public Wi-Fi networks. Mobile VPNs utilize secure protocols like IPsec or SSL/TLS to establish an encrypted connection, protecting sensitive data from potential threats or eavesdropping.
SSL/TLS VPN
SSL/TLS VPNs are widely used for secure remote access to corporate networks. By utilizing the SSL/TLS protocols, these VPNs create an encrypted connection between the client device and the VPN gateway. SSL/TLS VPNs provide a high level of security, authenticating both the client and the server, and can be accessed using a web browser or dedicated VPN client.
6. VPNs for Personal Use
While VPNs are commonly used in corporate settings, they also offer various benefits for personal use. Let’s explore some of these advantages.
Online Privacy and Anonymity
Using a VPN can significantly enhance your online privacy and anonymity. By encrypting your internet traffic and routing it through VPN servers, you can prevent your internet service provider (ISP), network administrators, or even hackers from monitoring your online activities. VPNs also mask your IP address, making it harder for websites, advertisers, or other entities to track your browsing behavior.
Bypassing Geographical Restrictions
With geographically restricted content becoming more prevalent, VPNs offer a solution for accessing blocked or regionally restricted websites and services. By connecting to a VPN server located in another country, you can appear as if you are browsing from that location. This can grant you access to content, streaming services, or online platforms that might be inaccessible in your region.
Secure Public Wi-Fi Connections
Public Wi-Fi networks, such as those found in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, are often unsecured and prone to security risks. Using a VPN on public Wi-Fi encrypts your data, protecting it from potential eavesdropping or malicious activity. VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, ensuring that your sensitive information, such as logins or credit card details, remains safe from prying eyes.
Torrenting and P2P File Sharing
If you engage in torrenting or peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing, a VPN can provide an additional layer of security and privacy. By masking your IP address and encrypting your traffic, VPNs help keep your activity anonymous, preventing your ISP or copyright enforcement agencies from monitoring or throttling your connection. However, it’s important to note that not all VPN providers condone or support illegal activities, so choose your VPN provider wisely.
7. VPNs for Gaming
VPNs can also be beneficial for gamers, enhancing their gaming experience and security. Let’s explore some advantages of using VPNs for gaming.
Reduced Latency
One of the main advantages of using a VPN for gaming is the potential for reduced latency or “ping.” VPNs can optimize the routing of internet traffic, potentially bypassing congested or high-latency routes. This can result in smoother gameplay, reducing lag and improving the overall gaming experience.
Protection against DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can disrupt online gaming by overwhelming a game server with a flood of traffic. By connecting to a VPN server, your IP address is masked, making it much harder for malicious individuals to launch DDoS attacks against you. VPNs provide an additional layer of protection and can help ensure uninterrupted gaming sessions.
Access to Region-Locked Games
Some game publishers release region-locked versions of their games, limiting access based on geographic location. By connecting to a VPN server in a region where the game is available, you can bypass these restrictions and access games that might otherwise be unavailable in your country. This is especially useful for gamers interested in trying out games before their official release or acquiring exclusive titles.
Improved Security for In-Game Transactions
Virtual goods, in-game currency, and other valuable assets in online gaming can be a prime target for hackers and scammers. By using a VPN, you can add an extra layer of security to your in-game transactions. VPNs encrypt your data and protect your connection, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to intercept or manipulate your gaming transactions.
8. Limitations and Challenges of VPNs
While VPNs offer numerous benefits, they also come with certain limitations and challenges. Let’s explore some of these aspects.
Internet Speed and Performance
One of the most common concerns when using a VPN is the potential impact on internet speed and performance. Encrypting and routing data through VPN servers can introduce additional latency and reduce overall connection speeds. While modern VPNs strive to minimize these effects, it’s important to choose a reliable VPN provider and connect to servers with optimal performance to mitigate any potential speed issues.
Compatibility Issues
Not all devices, operating systems, or networks are compatible with VPNs. While most platforms provide built-in VPN support, some older devices or operating systems might lack necessary protocols or configuration options. Additionally, certain networks may block VPN traffic or restrict access to VPN services. It’s essential to verify compatibility and ensure that your chosen VPN client has support for your specific device or operating system.
Trust and Reliability
When using a VPN, you are entrusting your internet traffic and potentially sensitive data to the VPN provider. It’s crucial to choose a reputable and trustworthy VPN service, as some providers may log user activity or even engage in questionable data practices. Privacy-conscious individuals should thoroughly research VPN providers, review their privacy policies, and opt for services that adhere to a strict no-logs policy.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The legal and ethical implications of using VPNs can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the intended usage. While VPNs are generally legal, certain countries have restrictions or regulations surrounding their use. Additionally, VPNs can be misused for illegal activities or to circumvent legitimate security measures. It’s important to understand and comply with the laws and regulations of your country when using a VPN.
Government Censorship and Surveillance
In some countries, VPN usage is tightly controlled or outright banned as a means to restrict access to information or monitor citizens’ online activities. Governments can employ various techniques to detect and block VPN traffic, making it challenging to maintain open access to the internet. It’s crucial to be aware of the legal landscape and potential risks when using a VPN in such regions.
9. VPNs and Net Neutrality
As the debate around net neutrality continues, VPNs play a significant role in preserving an open and neutral internet. Let’s explore their impact on net neutrality.
Ensuring Equal Access to the Internet
Net neutrality promotes equal access to online content, treating all internet traffic equally, regardless of the source or destination. VPNs, by encrypting and routing traffic through VPN servers, help mask the nature of internet traffic from internet service providers (ISPs), ensuring that they cannot discriminate or throttle specific types of traffic. VPNs enable users to access the internet freely and without unfair censorship.
Preventing Discrimination by ISPs
Some ISPs have been known to engage in discriminatory practices, such as blocking specific websites or throttling certain types of traffic. By using a VPN, users can bypass these discriminatory measures, effectively preventing ISPs from identifying and limiting access to specific websites, services, or platforms. VPNs enable users to maintain their online freedom while bypassing potential restrictions imposed by ISPs.
Threats to Net Neutrality
Net neutrality faces various threats in the modern digital age. ISPs may be tempted to prioritize certain types of internet traffic, creating “fast lanes” for certain websites or services. This could result in unequal access to online content, stifling competition and innovation. Additionally, governments and regulators may implement policies that restrict free access to information or engage in surveillance. VPNs play a vital role in circumventing these threats and preserving a neutral internet.
Role of VPNs in Preserving Net Neutrality
VPNs can act as a tool for preserving net neutrality by allowing users to maintain an open and unrestricted access to the internet. By encrypting and routing internet traffic through VPN servers, users can bypass discriminatory practices by ISPs and prevent government censorship. VPNs empower individuals to exercise their rights and maintain an unrestricted flow of information online.
10. Future of VPNs
As technology continues to advance, the future of VPNs looks promising. Let’s explore some potential advancements and trends on the horizon.
Increased Adoption and Awareness
As online privacy concerns grow and the need for secure connectivity becomes more apparent, the adoption of VPNs is expected to increase. More individuals and organizations are recognizing the importance of VPNs in safeguarding sensitive data and protecting online privacy. With increasing awareness and education, VPN usage is likely to become more mainstream.
Advancements in Encryption Technologies
Encryption is at the heart of VPN technology, and advancements in encryption algorithms and techniques are expected to improve the overall security of VPN connections. As quantum computing becomes more prevalent, VPNs may need to adopt post-quantum encryption algorithms to ensure long-term security. These advancements will continue to enhance the strength and reliability of VPNs.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies can play a significant role in enhancing VPN performance and security. VPNs could utilize AI and ML algorithms to optimize network routing, automatically select the best servers for specific locations, detect and mitigate potential security threats, or improve user authentication methods. Integration with AI and ML could revolutionize VPN technology.
Emergence of Decentralized VPNs
Decentralized VPNs (dVPNs) are an emerging trend in the VPN landscape. Unlike traditional VPNs that rely on centralized servers, dVPNs leverage blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks to create secure connections. Decentralized VPNs offer enhanced privacy and censorship resistance, as they distribute VPN infrastructure across multiple users, making it more challenging to track or block VPN traffic. The rise of dVPNs could pave the way for a more decentralized and democratized internet.
In conclusion, VPNs have evolved from humble beginnings to become an essential tool for both personal and corporate use. From their early development in X.25 networks to the emergence of advanced protocols like IPsec and SSL/TLS, VPNs have come a long way in providing secure and private communication over the internet. As individuals and organizations recognize the importance of online privacy, VPN usage is expected to grow, and the future holds exciting advancements in encryption, AI integration, and decentralized VPN technology.